Maximizing IT Investment Returns: Strategic Alignment of Information Technology towards Corporate Performances
American Journal of Applied Mathematics and Statistics. 2017, 5(2), 72-79. DOI: 10.12691/ajams-5-2-5 Published online: July 21, 2017
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Methodology
This study focuses on the relationship between strategic alignment of IT investment returns and corporate performance, and seeks supporting empirical evidence. Following are the study’s specific research objectives:
i. To establish whether closer alignment between business and IT strategies lead to increased returns on IT investments.
ii. To determine whether closer alignment between business and IT strategies lead to improved corporate performance.
iii. To determine the relationship between early adoption of new and emerging technology and business competitive advantage.
i. Does closer alignment between business and IT strategies significantly lead to increased returns on IT investments.
ii. Does closer alignment between business and IT strategies significantly lead to improved corporate performance.
iii. Is there any significant relationship between early adoption of new and emerging technology and business competitive advantage.
H10: Closer alignment between business and IT strategies does not lead to increased returns on IT investments. Against;
H11: Closer alignment between business and IT strategies leads to increased returns on IT investments.
H20: Closer alignment between business and IT strategies does not lead to improved corporate performance. Against;
H21: Closer alignment between business and IT strategies will lead to improved corporate performance
H30: There is no relationship between early adoption of new and emerging technology and business competitiveness. Against;
H31: There is a relationship between early adoption of new and emerging technology and business competitiveness.
Aggressiveness refers to the rate of adoption by a business in striving for resources to improve its market performance relatively faster than their competitors in the market.
Analysis refers to the expertise of problem solving by having a tendency to search deeper root cause of problems and to come up with best possible solution alternatives.
Defensiveness refers to defensive behavior in terms of emphasizing on cost reduction and consideration of business efficiency.
Futurity refers to reflection of temporal considerations in strategic decision making in terms of the relative emphasis of effectiveness considerations versus efficiency considerations.
Proactiveness refers to activeness behavior in participation in emerging industries and continuous search for market opportunities with regard to changing market trends.
Riskiness refers to the extent of riskiness reflected in various resource allocation decisions as well as choice of products and markets.
The research will adopt the descriptive research design using survey methodology for an empirical assessment of the relationship between strategic alignment on IT investment returns and corporate performance. Krueger & Casey 6 say the descriptive research design best enables collection of numerical data related to views, attitudes, perceptions and opinions from study respondents. The obtained data will be analyzed objectively to address the above stated research questions by asserting generalizations that can be drawn into conclusions.
The study is structured to have three sets of variables: dependent variable, independent variables and intervening variables. The dependent variable is the rating of returns on IT investments (Business returns).
The independent variables include STROBE dimensions including business alignment rating in: aggressiveness, analysis, defensiveness, futurity, proactiveness and riskiness. The other business alignment ratings investigated are: IT expertise level, satisfaction of IT values, IT system quality, new IT emerging innovations, and IT adoption.
Intervening variables include socio-demographic factors of IT and business stakeholders, including age, education level, gender, duration of IT usage and socio-economic status of IT professionals and IT managers.
The sample units in this study include: IT and Business Stakeholders, management & directors in banks, new customers and bank employees. Due to the largeconcentration of banking services in the Ajman, UAE and due to the lack of sufficient time and resources, a sample size of 150 individuals was deemed adequate for conducting this research. Mugenda (2003) suggested that a sample size of about 150-200 participants is suitable for an empirical descriptive research design. The sample size of 150 is mainly persons working in banks, bank customers and bank management teams.
4. Results
The collected data was filtered and coded using SPSS statistical software. Data reliability and validity was assessed using the Cronbach’s alpha test.
Reliability tests showed that most of the variables; overall variables (α=0.913), dependent factors (α=0.760), Independent factors including the STROBE dimensions (α=0.883), and the socio-demographic factors (α=0.814) possess greater than 0.7 alpha value of reliability. Thus, the data had more than the 70% reliability, validity, and feasibility attributes necessary for accurate analysis, allowing use of the information to find answers to our research questions.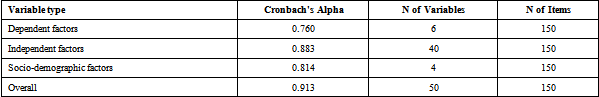
5. Summary: Results and Conclusions
Most of the study variables, the overall variables, dependent factors, and independent factors, including the STROBE dimensions and socio-demographic factors, possess an alpha value greater than 0.7 (α>0.7). Therefore, the data had above the necessary 70% reliability, validity and feasibility attributes for accurate analysis, allowing us to use the information to answer our study’s research questions.
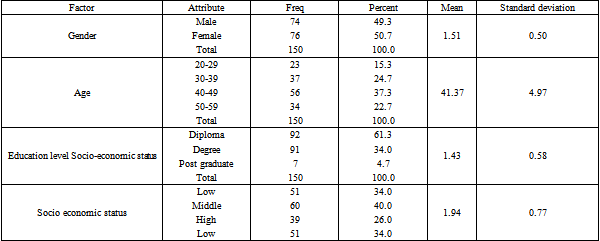
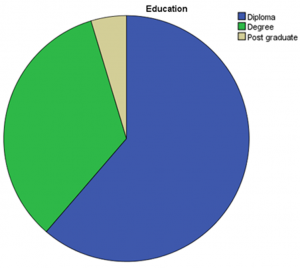
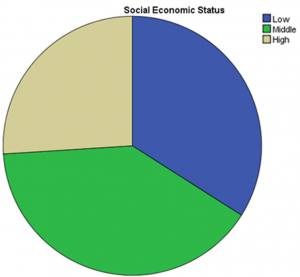
The genders of study respondents were 50.7% female and 49.3% male. This showed gender parity exists the study of strategic alignment on IT investment returns and corporate performance in banking sector. The age distribution of the study participants showed normality. The modal age group of the respondents was 40-49 years with an average the age (Mean=41.37 & SD= 4.97). A majority of respondents were diploma education level holders, followed by those with a degree education level. A minority held post graduate degrees. This shows that most of the banking stakeholders are of diploma education level. Finally, most respondents are of mid-level socio-economic status, followed by low socio-economic status. The lowest number of respondents were of high socio-economic status.
H10: Closer alignment between business and IT strategies does not lead to increased returns on IT investments. Against;
H11: Closer alignment between business and IT strategies leads to increased returns on IT investments.
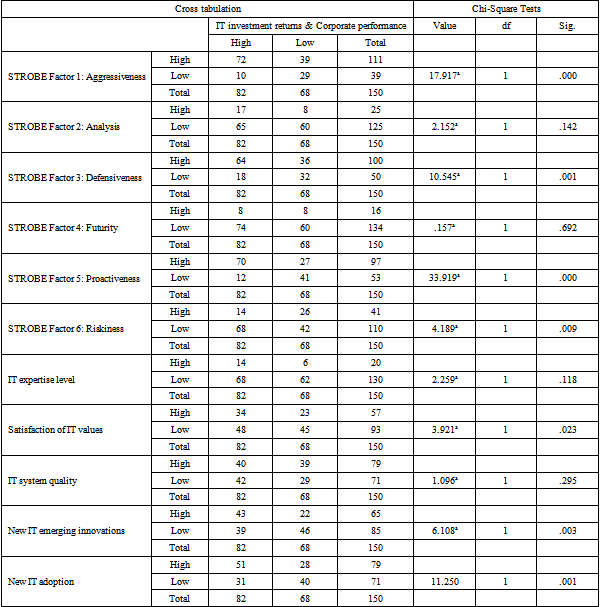
From our study results, the research showed that four of the STROBE dimensions including strategic alignment due to: aggressiveness, defensiveness, pro-activeness and riskiness had p-values that were less than 0.05. Therefore, the study rejects the null hypothesis (H10) and concludes that closer alignment between business and IT strategies leads to increased returns on IT investments.
H20: Closer alignment between business and IT strategies does not lead to improved corporate performance. Against;
H21: Closer alignment between business and IT strategies will lead to improved corporate performance..
The study also realized that strategic alignment ratings on satisfaction of IT values, new IT emerging innovations and new IT adoption had p-values less than 0.05 (p<0.05). Therefore, the research rejects the null hypothesis (H20) and concludes that closer alignment between business and IT strategies will lead to improved corporate performance.
H30: There is no relationship between early adoption of new and emerging technology and business competitiveness. Against;
H31: There is a relationship between early adoption of new and emerging technology and business competitiveness.
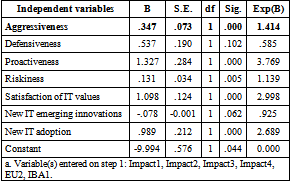
The study found that new IT emerging innovations and new IT adoption were significantly associated with business competitive advantage in Chi-square analysis. However, in binomial logistic analysis, it was found that new IT adoption was very significantly related to business competitive advantage. Therefore, the study general concludes that there is a positive relationship between early adoption of new and emerging technology and business competitiveness.

References
Chabrow, E. (March 24, 2003). IT staffs lack financial chops for project analysis, Information Week, 932, 20.
Chan, Y. E., Huff, S. L., Barclay, D. W., & Copeland, D. G. (1997). Business Strategic Orientation, Information Systems Strategic Orientation, and Strategic Alignment. Information Systems Research, 8(2): 125-150.
Hair, J.F., Anderson, R.E., Tatham, R.L. and Black, W.C. (1998), Multivariate Data Analysis, 5th ed., Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ.
Iman N, Hartono J. (2007). Strategic Alignment Impacts on Organizational Performance in Indonesian Banking Industry. Gadjah Mada International Journal of Business 2007; 9(2): 253-272.
Kothari, C. R. (2004). Research methodology: Methods and techniques. New Age International.
Krueger, R. A., & Casey, M. A. (2014). Focus groups: A practical guide for applied research. Sage.
Morgan, R. E., & Strong, C. A. (2003). Business Performance and Dimensions of Strategic Orientation. Journal of Business Research, 56(3): 163-176.
Mugenda, O. M. (2003). Research methods: Quantitative and qualitative approaches. African Centre for Technology Studies.
Ness, L. R. (2005). Assessing the relationships among information technology flexibility, strategic alignment, and information technology effectiveness. From ProQuest Dissertations & Theses database. (No. AAT 3178531).
Pierce, A.C. (2002). The effect of business and information technology strategic alignment on information technology investment returns and corporate performance. From ProQuest Dissertations & Theses database. (No. AAT 3058558).
Ross, J.W. & Breath, C.M. (2002). Beyond the Business Case: New Approaches to IT Investment, MIT Sloan Management Review, 51-59.
Shi, N. & Silvius, G. (2011). Enterprise IT governance, business value and performance measurement. Hershey, Pa: IGI Global (701 E. Chocolate Avenue, Hershey, Pennsylvania, 17033, USA.
Singh, A. & Desai, B. (2012). Strategic Business Alignment: A study of role of IT in Strategic Business Alignment in Banking sector of India. Global Journal for Research Analysis, 2, 1, 98-101.
Tallon, P. P., & Kraemer, K. L. (2003). Using flexibility to enhance the alignment between information systems and business strategy: Implications for IT business value. Center for Research on Information Technology and Organizations (CRITO), University of California, Irvine.
Venkatraman, N. (1989). Strategic Orientation of Business Enterprises: The Construct, Dimensionality, and Measurement. Management Science, 35 (8): 942-962.
